8th Class Science Force and Pressure (English Medium)
NMMS Exam Test Series
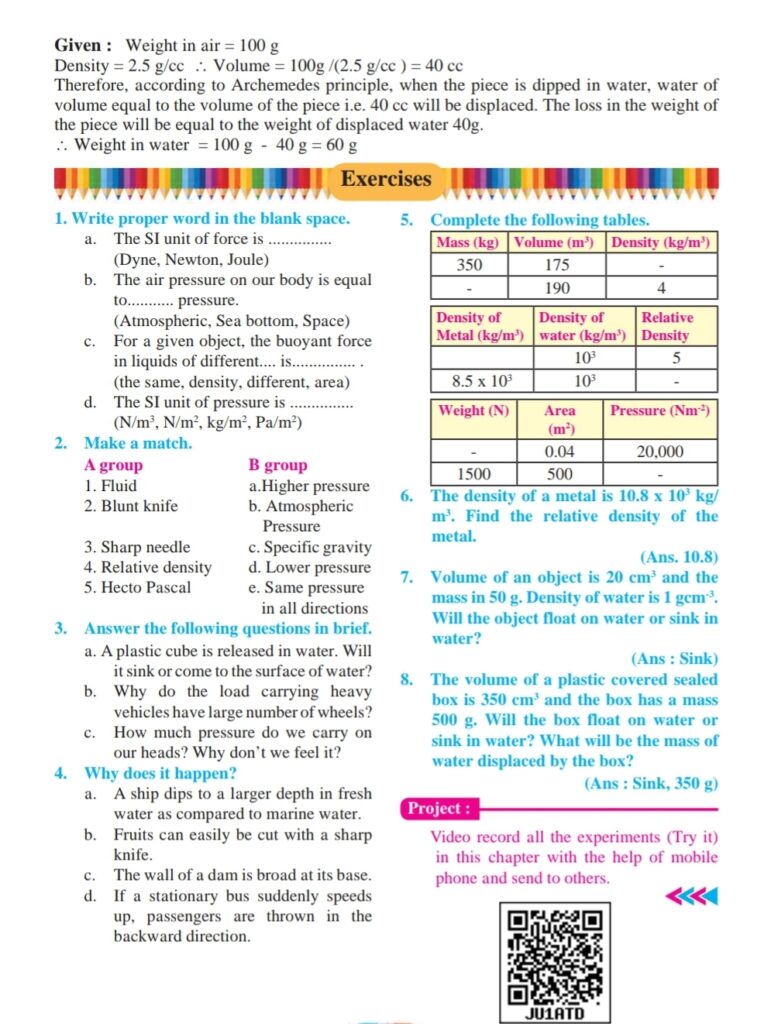
1)Will a block of mass 200 g and volume 400 cm³ float or sink in water?
- The object will float on water
- The object will not float on water
- The object will not sink in water
- The object will sink in water
2)A force that acts between two objects even if the two objects are not in contact is called a ——— force.
- contact
- Non-Contact
- balanced
- Unbalanced
3)The air pressure on our body is equal to the —————– pressure.
- sea bottom
- on hill
- atmospheric
- space
4)If the density of a metal is 10.8 X 10³ kg/m³, what is the relative density of that metal?
- 1.07
- 10.7
- 10.8
- 1.08
5)Which device is used to determine the purity of a sample of milk?
- Lactometer
- Voltmeter
- hydrometer
- submarine
6)The SI unit of pressure is called———–
- erg
- joule
- pascal
- newton
7)Which of the following quntity is expressed in pascal?
- mass
- velocity
- Pressure
- force
8)—————– is the ratio of the density of the substance to the density of water?
- specific gravity
- gravity
- acceleration
- None of these
9)—————– force is elecrtomgnetic in origin.
- contact
- Non-Contact
- gravitational
- frictional
10)At a dpth ‘h’ below the free surface of a liquid,the pressure exerted by the liquid is —————.
- mg
- hpg
- phg
- pascal
11)Atmospheric pressure ——— with altitude.
- remains same
- decreases
- increases
- None of these
12)A plastic cube is released in water.Will it sink or come to the surface of water?
- It will sink into the water.
- Both A and B are correct
- None of these
- It will come to the surface of water.
13)Keeping the surface area constant, if the applied force is doubled,the pressure ———————-.
- remains the same
- becomes four times
- becomes double
- becomes half
14)Which of the following is not working on Archimedes principle?
- submarine
- hydrometer
- lactometer
- Voltmeter
15)A stationary object on which no force is acting,remains stationary .An object in motion continues to move with the same speed and direction when no force is acting on it .Is it the ———————- law of motion.
- Newton’s third law
- Newton’s second law
- None of these
- Newton’s first law
16)Density of water is —– g/cm³.
- 1
- 10
- 100
- 1000
17)Which of the following is a vector quantity?
- Force
- density
- pressure
- mass
18)For a given object,the buoyant force in liquids of different ———–is the same.
- density
- equl
- area
- different
19)The SI unit of force is —————-.
- Newton
- dyne
- joule
- pascal
20)The pascal is the unit of —————————-.
- velocity
- force
- Pressure
- mass
21)A force that acts through a direct contact of two objects or via one more object is called a ——— force.
- contact
- balanced
- Unbalanced
- Non-Contact
22))1 atmosphere=————————-.
- 110 X 10²N/m
- 101 X 10³Pa
- 101 X 10²N/m²
- None of these
23)1 bar =——————-
- 10⁵ N/m
- 10⁵ N/m²
- 10²N/m²
- 10²N/m
24)Which of the following is working on Archimedes principle?
- Galvanometer
- Lactometer
- Voltmeter
- Ameter
25)The force and weight have the —————-unit.
- same
- constant
- different
- None of these
26)Which of the following is a scalar quantity?
- velocity
- Weight
- force
- Density
27) If a force of 1000 N is applied to a surface of area 50 cm X 20 cm, what will be the pressure at its bottom?
- 10⁴ N/m²
- 10⁵ N/m²
- None of these
- 10³ N/m²
28)The force exerted perpendicularly on a unit area is called —————–
- Pressure
- motion
- speed
- magnitude
29)Which device is used to determine the density of a liquid?
- Voltmeter
- hydrometer
- Lactometer
- submarine
30)The SI unit of density is ——————.
- N/m²
- kg/m³
- kg/m²
- pa/m²
31)Unbalanced force produces ————— in the body.
- speed
- acceleration
- motion
- None of these
32)Which of the following has more inertia?
- Rs.10 coin
- A and B both
- Rs.1 coin
- None of these
33)If the relative density of body is greater than1,will it float in water?
- It will not sink into the water.
- It will not float in water.
- It will float in water.
- It will sink into the water.
34)The tendency of an object to remain in its existing state is called its——————.
- acceleration
- inertia
- direction
- magnitude
35)In atmospheric science the unit for pressure is called—————–.
- bar
- erg
- pascal
- None of these
36)The buoyant force due to a liquid is proportional to the ————— due to gravity.
- acceleration
- motion
- None of these
- speed
37)If two or more forces act on a body such that their resultant is not zero,the resultant is an —————- force.
- Non-Contact
- contact
- balanced
- Unbalanced
38) —————- is a physical quantiy that changes the state of rest.
- Energy
- Force
- Power
- Motion
39)The ——————- of material is usful to determine its purity.
- weight
- size
- density
- mass
40)If body is acted upon two forces,equal in magnitude,opposite in direction and having the same line of action,the forces are called —————- forces.
- Unbalanced
- Non-Contact
- contact
- balanced
41)If a ball at rest on the ground is kicked, it starts moving is an example of ————— force.
- frictional
- None of these
- non contact
- contact
42)Which of the following is an example of contact force?
- a boy playing football is cicking the ball away.
- a coconut if alling from the coconut tree.
- a reluctant dog is being pulled by his master.
- None of these
43)The earth revolves around the sun is an example of —————– force.
- contact
- non contact
- None of these
- frictional
44)A———– is a substance which can flow.
- gas
- Fluid
- solid
- None of these
45)If the density of a metal is 10.8 X 10³ kg/m³, what is the relative density of that metal?
- 1.07
- 1.08
- 10.8
- 10.7
What is a force?
Contact and Non contact forces : In fig. 3.1 a car moves in forward direction when a man
applies force from behind. A reluctant dog is being pulled by his master and a boy playing
football is kicking the ball away. What do you observe from these? A force acts on two bodies through an interaction between them.
A stationary object on which no force is acting, remains stationary. An object in motion continues to move with the same speed and direction when no force is acting on the object.
This is Newton’s first law of motion.
As seen in fig 3.2, iron nails get attracted to the pole of a magnet due to magnetic force.
A coconut is falling from the coconut tree. Objects are attracted to the earth due to the force of gravity. When a comb gets rubbed against hair, small pieces of paper
kept on a table get attracted to the comb. The
comb has an electrostatic charge and there is
an induced opposite charge on the pieces of
paper and the pieces stick to the comb.
In fig 3.1 a force is seen to act through a direct contact of the objects or via one more
object. Such a force is called ‘Contact force’.
In fig 3.2, a force is applied between two objects even if the two objects are not in
contact, such a force is called a ‘Non contact
force’.
Muscular force is an example of contact
force and is applied to objects with the help
of our muscles. It is applied in several cases
such as lifting, pushing, pulling. On the contrary, forces like magnetic force,
gravitational force, electrostatic force act
without a contact. Therefore, these are the
examples of non contact forces.
When a ball is kept on a table and
pushed a little, it moves ahead and gets slow
and stops. A car running on a plane road
travels some distance and stops after the
engine is switched off. This is because of the
force of friction between the ground surface
and the object in motion. In the absence of
frictional force, the object would have
remained in motion. Frictional force is very
useful in daily life. While walking, we push
the ground behind with our feet. In the
absense of friction, we will slip and will not
be able to walk. All the objects in motion
have a frictional force acting on them which
is acting in the direction opposite to the
direction of motion. You must have seen that one tends to slip over banana peel on the street.
Similarly one can slip due to mud. Both these examples occur due to reduced friction.
Make a list of some more examples in which contact and non contact forces are applied. Write the types of force.
Balanced and unbalanced force
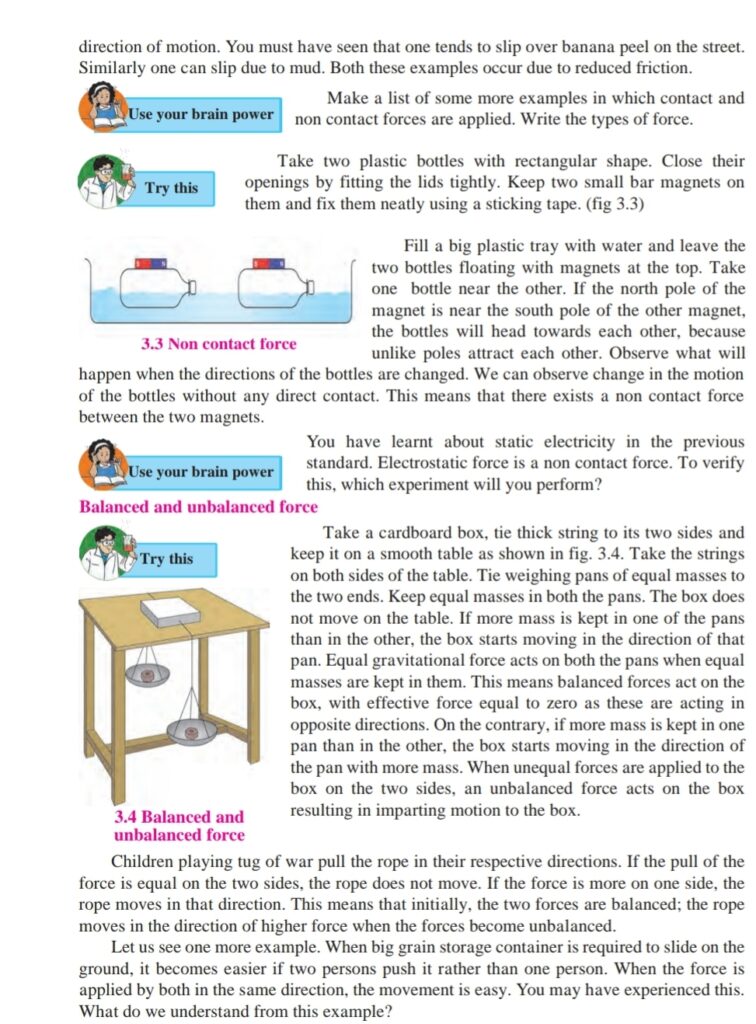
Take two plastic bottles with rectangular shape. Close their openings by fitting the lids tightly. Keep two small bar magnets on
them and fix them neatly using a sticking tape. (fig 3.3)
Fill a big plastic tray with water and leave the
two bottles floating with magnets at the top. Take
one bottle near the other. If the north pole of the magnet is near the south pole of the other magnet,
the bottles will head towards each other, because unlike poles attract each other. Observe what will happen when the directions of the bottles are changed. We can observe change in the motion of the bottles without any direct contact. This means that there exists a non contact force between the two magnets.
You have learnt about static electricity in the previous standard. Electrostatic force is a non contact force. To verify this, which experiment will you perform?
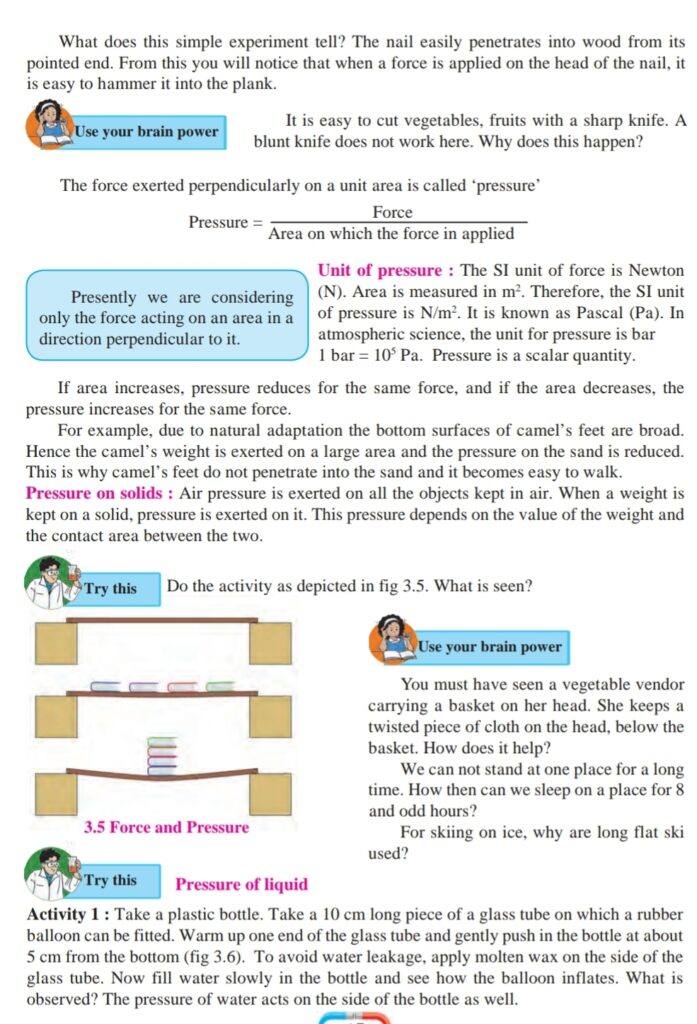
Take a cardboard box, tie thick string to its two sides and keep it on a smooth table as shown in fig. 3.4. Take the strings
on both sides of the table. Tie weighing pans of equal masses to the two ends. Keep equal masses in both the pans. The box does
not move on the table. If more mass is kept in one of the pans than in the other, the box starts moving in the direction of that
pan. Equal gravitational force acts on both the pans when equal masses are kept in them. This means balanced forces act on the
box, with effective force equal to zero as these are acting in opposite directions. On the contrary, if more mass is kept in one pan than in the other, the box starts moving in the direction of the pan with more mass. When unequal forces are applied to the
box on the two sides, an unbalanced force acts on the box resulting in imparting motion to the box.
Children playing tug of war pull the rope in their respective directions. If the pull of the
force is equal on the two sides, the rope does not move. If the force is more on one side, the
rope moves in that direction. This means that initially, the two forces are balanced; the rope
moves in the direction of higher force when the forces become unbalanced.
Let us see one more example. When big grain storage container is required to slide on the
ground, it becomes easier if two persons push it rather than one person. When the force is
applied by both in the same direction, the movement is easy. You may have experienced this.
What do we understand from this example?